Study of functional outcome in low grade spondylolisthesis operated by pedicular screw instrumentation and fusion
Abstract
Background: Functional outcome following instrumental spinal surgery for spondylolisthesis in physically energetic patients is crucial. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the functional outcome of low-grade spondylolisthesis accompanied by low back pain with or without radiculopathy, with standard surgical procedure posterior lumbar interbody fusion with instrumentation.
Method: In this study total of 40 patients were operated on for low-grade spondylolisthesis by posterior stabilization using a pedicular screw rod system and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. All the patients were followed up till 6 months after surgery and functional outcomes were noted.
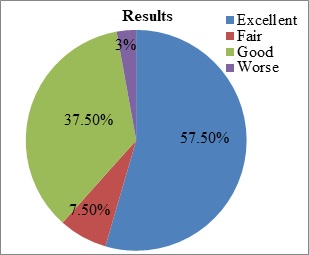
Results: Assessment of this series it was observed that, 57.5% of the patient had excellent outcome, 37.5% had a good outcome and 97.5% of the study population had satisfactory outcome (improvement in clinical results). There was a significant improvement in pain intensity, walking, lifting, standing, sleeping after surgery. The mean ODI difference between preoperative and post-operative at 6 months follow up was 36.12% (16.75). In the outcome, 62.5% of the patient consisted of severe disability and 32.5% were with moderate disability (total-95%) while postoperative 87.5% were with a minimal disability and only 2.5% of the study population had worsened i.e crippled.
Conclusion: The study concluded that surgery in form of decompression with instrumentation and posterior lumbar interbody is a safe and effective method to treat spondylolisthesis.
Downloads
References
Rowe GG, Roche MB. The aetiology of the separate neural arch. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1953;35:102-10.
Tenny S, Gillis CC. Spondylolisthesis. [Updated 2020 Jul 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430767/
Chaitanya, M., Mittal, A., Rallapalli, R., Teja, R. and Prasad, Y.S. (2015) Surgical Management of Spondylolisthesis by Pedicular Screw Rod System and Postero-Lateral Fusion. Open Journal of Orthopedics 2015; 5:163-174.
Christensen FB, Hansen ES, Laursen M, Thomsen K,Bunger CE. Long-term functional outcome of pedicle screw instrumentation as support for posterolateral spinal fusion. A randomized clinical study with a 5-year follow-up.Spine 2002;27:1269-1277.
Shivakumar HB, Channappa TS, Singh A. Functional Outcome of Lumbo-Sacral Spondylolisthesis-Posterior Stabilisation with Moss-Miami Instrumentation and Spinal Fusion.” Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2015;4(93): 15819-15822.
Molinari RW, Sloboda JF, Arrington EC, et al., Low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis treated with instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion in US servicemen. J Spinal Disord Tech 2005;18(suppl 1):S24–9.
Yizhar Floman, Michael A. Millgram; Instrumented Slip Reduction and Fusion for Painful Unstable Isthmic Spondylolisthesis in Adults; J Spinal Disord Tech 2008;21:477–483.
Labelle H, Mac-Thiong JM, Roussouly P. Spino-pelvic sagittal balance of spondylolisthesis: a review and classification. Eur Spine J 2011; 20(Suppl 5): 641-6.
Mohammad A, Ahmad Y. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Spondylolisthesis and Degenerative Segmental Instability. Surgical and Radiological Outcome.Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery 2015;30(3):213-220.
Cheng CL, Fang D, Lee PC, Leong JC: Anterior spinal fusion for spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis. Long term results in adults. J bone Joint Surg Br 1989;71:264-7.
Debnath, Ujjwal K. et al. Interbody Fusion in Low Grade Lumbar Spondylolsithesis: Clinical Outcome Does Not Correalte with Slip Reduction and Neural Foraminal Dimension.Asian Spine Journal 2016;10(2):314–320.
Gaetani P, Aimar E, Panella L, Levi D, Tancioni F, Di Ieva A, Debernardi A, Pisano P, Rodriguez y Baena R. Functional disability after instrumented stabilization in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: a follow-up study. Funct Neurol. 2006;21(1):31-7.
Pasha IF, Qureshi MA, Haider IZ, Malik AS, Qureshi MA, Bin Tahir U. Surgical treatment in lumbar spondylolisthesis: experience with 45 patients. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2012;24(1):75-8.
Park Y, Ha JW, Lee YT, Oh HC, Yoo JH, Kim HB. Surgical outcomes of minimallyinvasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of spondylolisthesis and degenerative segmental instability. Asian Spine J. 2011;5(4):228-36.
Liu ZD, Li XF, Qian L, Wu LM, Lao LF, Wang HT. Lever reduction using polyaxialscrew and rod fixation system for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: technique and clinical outcome. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:29.
Kaftandziev I, Trpeski S, Filipce V, Arsovski O, Hasani I, Nikolov L et al. Operative treatment of degenerative lumbar spine spondylolisthesis. PRILOZI. 2015;36(1):129–135.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


