A study to find the utility of MRI in the evaluation of painful hip joints
Abstract
Introduction: Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is a valuable tool in the evaluation of hip disorders. With these, a study was conducted to assess the role of MRI in the early evaluation of painful hip joints.
Materials and Methods: It was a cross-sectional study conducted in the department of Radiodiagnosis, GSL Medical College, Rajahmundry. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee. Patients presenting with acute or chronic hip pain pathology of all age groups, both gender who referred for MRI were included in the study. Imaging has been done with 1.5 Tesla Philips Achieva machines using abdominal surface coils and spine coils.
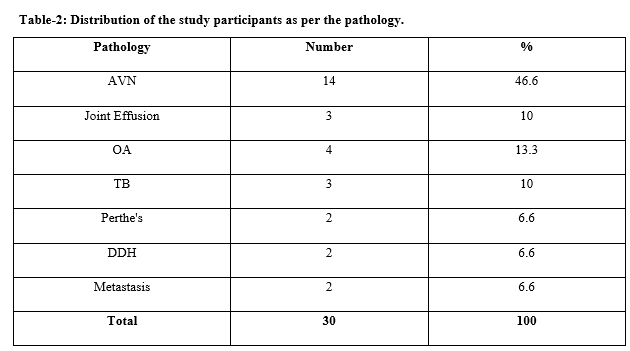
Results: Out of the 30 participants, avascular necrosis was diagnosed in 46.6% (14) participants, joint effusion in 10% (3) cases, osteoarthritis (OA) in 4 (13.3%) cases, tuberculosis (TB) in 10% (3), 6.6% (2) each was diagnosed to be Perthe’s, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) and metastasis, respectively. All the pathological findings were diagnosed using MRI also.
Conclusion: MRI helps in the evaluation of the involvement of articular cartilage in the form of T2W hyperintensity. It also helps in the evaluation of soft tissue involvement along with the detection of bone marrow edema.
Downloads
References
Manaster BJ. Adult Chronic Hip Pain: Radiographic Evaluation. Radiographics. 2000;20:S3-S25.
Gabriel H, Fitzgerald SW, Myers MT, Donaldson JS, Andrew K, Poznanski. MR Imaging of Hip Disorders. Radiographics. 1994;14:763-781.
Shih TT, Su CT, Chiu LC, Erickson F, Hang YS, Huang KM. Evaluation of hip disorders by radiography, radionuclide scanning and magnetic resonance imaging. J Formos Med Assoc. 1993;92(8):737-744.
Khanna AJ, Yoon TR, Mont MA, Hungerford DS, Bluemke DA. Femoral head osteonecrosis: detection and grading by using a rapid MR imaging protocol. Radiol. 2000;217(1):188-192.
Robinson Jr HJ, Hartleben PD, Lund G, Schreiman J. Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Accuracy compared with radiographs, core biopsy, and intraosseous pressure measurements. J Bone Joint Surg. 1989;71(5):650-663.
Huang GS, Chan WP, Chang YC, Chang CY, Yu-Chen C, Joseph SV. MR imaging of bone marrow edema and joint effusion in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head: relationship to pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181(2):545-549.
Yang WJ, Im SA, Lim GY, Chun HJ, Jung NY, Sung MS, et al. MR imaging of transient synovitis: differentiation from septic arthritis. Pediatric Radiol. 2006;36(11):1154-1158.
Mitchell DG, Rao V, Dalinka M, Spritzer CE, Gefter WB, Axel L, et al. MRI of joint fluid in the normal and ischemic hip. Am J Roentgenol. 1986;146(6):1215-1218.
Boniatis I, Costaridou L, Cavouras D, Kalatzis I, Panagiotopoulos E, Panayiotakis G. A morphological index for assessing hip osteoarthritis severity from radiographic images. Brit J Radiol. 2008;81(962):129-136.
Li KC, Higgs J, Aisen AM, Buckwalter KA, Martel W, McCune WJ. MRI in osteoarthritis of the hip: gradations of severity. Magnetic Resonan Imag. 1988;6(3):229-236.
Xu L, Hayashi D, Roemer FW, Felson DT, Guermazi A. Magnetic resonance imaging of subchondral bone marrow lesions in association with osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;42(2):105-118.
Shrestha OP, Sitoula P, Hosalkar HS, Banskota AK, Spiegel DA. Bone and joint tuberculosis. University of Pennsylvania Orthopaed J. 2010;20:23-28.
Buxi TB, Sud S, Vohra R. CT and MRI in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Indian J Pediatr. 2002;69(11):965-972.
Beltran LS, Rosenberg ZS, Mayo JD, De Tuesta MD, Martin O, Neto LP, et al. Imaging evaluation of developmental hip dysplasia in the young adult. Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(5):1077-1088.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


