A study on nephropathy in type2 diabetes individuals in coastal Andhra Pradesh, India
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes nephropathy (DN) is an important, life-threatening microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus (DM). With this, a study was conducted to find the association between type 2 DM and DN.
Materials and Methods: The study was conducted in the department of general medicine, GSL Medical College. Type 2 diabetic subjects who attended the outpatient and inpatient wards, aged > 30 years were included in the study, known renal disease/ were not considered. Albumin creatinine ratio was measured by immune turbidometry using a microalbuminuria test kit provided by ERBA MANHEIM GERMANY. Serum creatinine was done by creatininase enzymatic method, eGFR was calculated using the CKD-EPI equation. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
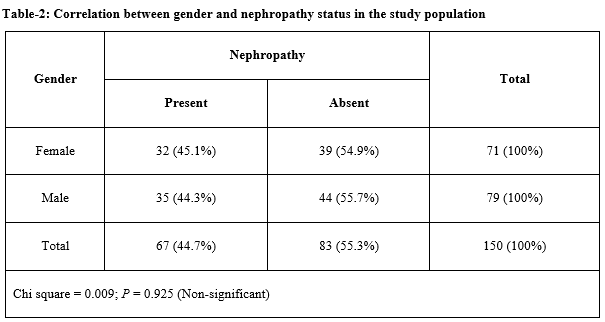
Results: A total of 150 DM participants were included in the study; mean serum creatinine was 1.59 + 1.25 with a range from 0.4 to 8.7 mg/dl and mean eGFR of the study participants was 73.65 + 40.428 ml/min/m2 with a range from 7 to 162 ml/min/m2. DN was detected in 45% (67) participants.
Conclusions: The present study reveals that there was significant evidence to support that microalbuminuria or proteinuria in patients with diabetes is a potential risk factor not only for kidney function impairment but also as a marker for high risk of cardiovascular complications.
Downloads
References
Zhenhua He. Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Patients. J Mol Biomark Diag. 2016;7:5. doi: 10.4172/2155-9929.1000295.
Ragnar Pálsson, MD and Uptal D. Patel, MD Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetic Kidney Disease Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014;21(3):273-280. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2014.03.003.
Alvin C. Powers, Diabetes Mellitus: Complications Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th edition, 2015.
Mogensen CE, Christensen CK, Vittinghus E. The stages in diabetic renal disease: with emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1983;32(2):64-78. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.S64.
Unnikrishnan R, Rema M, Pradeepa R. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic nephropathy in an urban south Indian population: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 45). Diabetes Care. 2007;30(8):2019-2024. doi: 10.2337/dc06-2554.
Shaw PK, Baboe F, van Es LA, van der Vijver JC, van de Ree MA, de Jonge N, et al. South-Asian Type 2 Diabetic Patients Have Higher Incidence and Faster Progression of Renal Disease Compared With Dutch- European Diabetic Patients, Diabetes Care. 2006;29(6):1383-1388. doi: 10.2337/dc06-0003.
R. Retnakaran Cromme, R., Szekessy, T. Risk Factors for Renal Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study. Diabetes. 2006;55(6):1832-1839. doi: 10.2337/db05-1620.
Wirta OR, Pasternack AI, Oksa HH, Mustonen JT, Koivula TA, Helin HJ, et al. Occurrence of late specific complications in type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 1995;9(3): 177-185. doi: 10.1016/1056-8727(94)00034-l.
Collins VR, Dowse GK, Plehwe WE, Imo TT, Toelupe PM et al. High prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in Polynesians of Western Samoa. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(8):1140-1149. doi: 10.2337/diacare.18.8.1140.
Krairittichai U. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic nephropathy among Thai patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011;94(2):1-5.
Hong D, Zheng T, Jia-qing S, Jian W, Zhihong L, Lei-shi L. Nodular glomerular lesion: A later stage of diabetic nephropathy? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;78(2):189-195. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2007.03.024.
Miyazato J, Horio T, Takiuchi S, Kamide KO, Sasaki S, et al. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic renal failure: impact of diabetes mellitus, Diabetes UK. Diabetic Med. 2005;22(6): 730-736. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2005.01500.x.
Caramori M, Fioretto P, Mauer M. The need for early predictors of diabetic nephropathy risk: is albumin excretion rate sufficient? Diabetes. 2000;49(9):1399-1408. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.9.1399.
Younes N, Hanai K, Suzuki K. Comparison of Urinary Albumin-Creatinine Ratio and Albumin Excretion Rate in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications study clinic. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5(7):1235-1242. doi: 10.2215/CJN.07901109.
Fisher H. Comparison of Associations of Urine Protein-Creatinine Ratio Versus Albumin-Creatinine Ratio with Complications of CKD: A Cross-sectional Analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(6):313-320. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.07.013.
Watanabe Y. A Cross-sectional Survey of Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic, Patients at Four Urban Diabetes Clinics. Inter Med. 2009;48(6):411-414. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.48.1691.
Sanjeev Kumar, Brenner BM, Toto RD. Correlation of DN and HbA1C in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients of Western UP. Inter J Sci Res. 2014;4(12):221-225. doi: 10.21276/ijcmr.2019.6.4.40.
Birakta Debbarma, Mohanram A, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S, Keane WF. Significance of Microalbuminuria in Newly Diagnosed type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. IOSR J Den Med Sci. 2015;14(8):40-47. doi: 10.9790/0853-14814047.
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang Y, Castro AF, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(9):604-612. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


