Estimation of prostate size by trans-rectal ultrasound and its correlation with DRE and endoscopic grading
Abstract
Aim: Digital rectal examination (DRE) grading and the grade of prostatomegaly on cystoscopy are routinely used in clinical practice, but its correlation to prostate volume is understudied. This study was done to assess the correlation of DRE and endoscopic grading with the prostate volume on trans-rectal ultrasound (TRUS).
Materials and Methods: This study was carried out in 101 eligible patients with prostatomegaly. Each patient was evaluated for three parameters, prostate volume by TRUS examination, DRE and endoscopic grading on cystoscopy. Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated to find the correlation between variables, p<0.05 was taken to be statistically significant. Data were analyzed using the Epi Info (TM) 7.2.2.2.
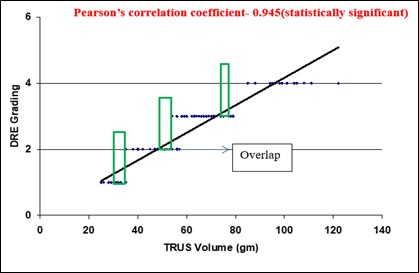
Results: Significant positive correlation (p<0.001) was found between TRUS Volume and DRE grading (Pearson Correlation=0.945) and TRUS volume and Endoscopic grading (Pearson Correlation=0.949). Both the grading were also significantly positively correlated (Pearson Correlation=0.989, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our attempt for correlating the digital rectal grading and endoscopic grading with prostate volume is satisfactorily validated in the clinical setting. These grades are sufficient to provide a rough estimation of the prostate volume and to classify patients with prostatomegaly.
Downloads
References
Chaple CR, MacDiarmid SA. Voiding difficulty. In: Chaple C, MacDiarmid S, eds, Urodynamics. Made easy, 2 ed, Vol. 1. Chapt 4. London: WB Saunders, Harcourt Publishers Limited 2000, pp. 75-76.
Lodh B, Sinam RS, Singh KA. Digital rectal grading of benign prostatic hyperplasia: Where does it stand today? J Mahatma Gandhi Inst Med Sci. 2016;21(2):40-45. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-9903.178104.
Romero F, Romero A, Filho T, Kulysz D, Oliveira F, Filho R. The prostate exam. Health Edu J. 2011;71(2):239-250. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0017896911398234.
Roehrborn C, Chinn H, Fulgham P, Simpkins K, Peters P. The Role of Transabdominal Ultrasound in the Prostatic Hypertrophy. J Urol. 1986;135(6):1190-1193. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)46032-0.
Barnes R.W., Bergman R.T., Hadley H.L. Indications for endoscopic surgery. In: Endoscopy. Encyclopedia Urol. 1959 vol 6. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Terris MK, Stamey TA. Determination of prostate volume bytransrectal ultrasound. J Urol. 1991;145(5):985-987. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)38508-7.
Madersbacher S, Marberger M. Is transurethral resection of theprostate still justified? BJU Int. 1999;83(3):227‑237. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00908.x.
Aus G, Bergdahl S, Hugosson J, Norlén L. Volume determinationsof the whole prostate and of adenomas by transrectal ultrasoundin patients with clinically benign prostatic hyperplasia: correlationof resected weight, blood loss and duration of operation. Br J Urol. 1994;73(6):659‑663. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410x.1994.tb07552.x.
Boyle P, Gould AL, Roehrborn CG. Prostate volume predicts outcome of treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with finasteride: meta‑analysis of randomized clinical trials. Urol. 1996;48(3):398‑405. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(96)00353-6.
Bates TS, Reynard JM, Peters TJ, Gingell JC. Determination ofprostatic volume with transrectal ultrasound: A study of intraobserverand interobserver variation. J Urol. 1996;155(4):1299-1300. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66250-5.
Kim S, Kim S. Correlations between the Various Methods of Estimating Prostate Volume: Transabdominal, Transrectal, and Three-Dimensional US. Korean J Radiol. 2008;9(2):134-139. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.3348%2Fkjr.2008.9.2.134.
Roehrborn C, Girman C, Rhodes T, Hanson K, Collins G, Sech S et al. Correlation between prostate size estimated by digital rectal examination and measured by transrectal ultrasound. Urol. 1997;49(4):548-557. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(97)00031-9.
Streich U, Rockstroh H, Anger G, Weck B, Millner R. Objective determination of prostate size with ultrasound. Z Urol Nephrol. 1980;73(8):577‑581.
Smith HJ, Haveland H. Pre‑operative and post‑operativevolumetry of the prostate by transabdominal ultrasonography. Br J Urol. 1982;54(5):531‑535. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410x.1982.tb13583.x.
Cheng WC, Ng FC, Chan KC, Cheung YH, Chan WL, Wong SW. Interobserver variation of prostatic volume estimation with digitalrectal examination by urological staffs with different experiences. Int Braz J Urol. 2004;30(6):466‑471. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1677-55382004000600003.
Lane TJ. A note on rectal examination of the adenomatous prostate. Ir J Med Sci. 1940:15:322-326.
Tsui KH, Liu CY, Lui JM, Lee ST, Tan RP, Chang PL. Direct observation of procedural skills to improve validity of students’ measurement of prostate volume in predicting treatment outcomes. Urol Sci. 2013;24(3):84-88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urols.2012.09.001.
Reis LO, Simão AF, Baracat J, Denardi F, Gugliotta A. Digitalrectal examination standardization for inexperienced hands: Teaching medical students. Adv Urol. 2013;2013:797096. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/797096.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


