Pancreatic ketoacidosis-a rare case report
Abstract
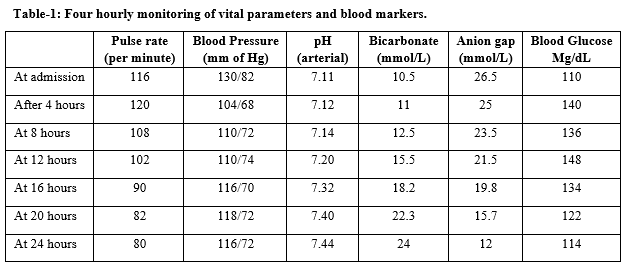
Euglycemic Pancreatic Ketoacidosis is a syndrome of high anion gap acidosis in which the high anion gap is due to elevated serum ketone bodies comprising of acetone, aceto- acetate and beta hydroxyl-butyrate, due to increased peripheral adipose tissue breakdown by elevated serum lipase as a consequence of acute pancreatitis with normal blood glucose levels. There are multiple causes for ketonuria and/or ketonemia with or without acidosis like uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, usually of the insulin dependent type (diabetic ketoacidosis), lactic acidosis, prolonged starvation (starvation ketosis), ethanol ingestion (alcoholic ketoacidosis), sepsis, pregnancy and vomiting. Our patient was not a known diabetic and his blood glucose were always within normal limits, so this ketoacidosis cannot be attributed to Diabetes Mellitus. It cannot be attributed to starvation as our patient was not fasting when he got admitted and furthermore ketoacidosis is not a frequent manifestation of starvation adding to it that we transfused adequate amount of DNS and resumed oral intake during our observation period. It cannot be attributed to vomiting as our patient had only two episodes of vomiting. Our patient does not have any liver or kidney pathology and there is no history or evidence of alcohol intoxication. But, acute pancreatitis without diabetes-mellitus, causing ketoacidosis is a very rare presentation which is caused by high levels of pancreatic lipase in the circulation.
Downloads
References
Eckerwall G, Olin H, Andersson B, Andersson R. Fluid resuscitation and nutritional support during severe acute pancreatitis in the past: what have we learned and how can we do better?. Clinical Nutrition. 2006;25(3):497-504. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2005.10.012.
Kabadi UM. Pancreatic ketoacidosis: ketonemia associated with acute pancreatitis. Postgraduate Med J. 1995;71(831):32-35. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1136%2Fpgmj.71.831.32.
Kabadi UM. Pancreatic ketoacidosis (kabadi syndrome) mimicking diabetic ketoacidosis. Endocrine Prac. 2015;21(10):1184-1185. doi: https://doi.org/10.4158/1934-2403-21.10.1184.
Prater J, Chaiban JT. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis with acute pancreatitis in a patient not known to have diabetes. AACE Clinic Case Rep. 2015;1(2):e88-e91. doi: https://doi.org/10.4158/EP14182.CR.
Rawla P, Vellipuram AR, Bandaru SS, Raj JP. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. Endocrinol, Diab Metabol Case Rep. 2017;2017(1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1530/EDM-17-0081.
Thawabi M, Studyvin S. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis, a misleading presentation of diabetic ketoacidosis. North Am J Med Sci. 2015;7(6):291-294. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.157490.
Modi A, Agrawal A, Morgan F. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: a review. Curr Diab Rev. 2017;13(3):315-321. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399812666160421121307.
Pillai V. A case of euglycemic pancreatic ketoacidosis-a case report. Univer J Medicine Med Special. 2018;4(2):13-15.
Hurrell FE, Drobatz KJ, Hess RS. Beta‐hydroxybutyrate concentrations in dogs with acute pancreatitis and without diabetes mellitus. J Vet Int Med. 2016;30(3):751-755. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fjvim.13947.
Kabadi UM. Pancreatic ketoacidosis: ketonemia secondary to increased circulating lipase of acute pancreatitis. Diab Res. 1999;34(1):1-7.
Kabadi UM. Pancreatic ketoacidosis: Imitator of diabetic ketoacidosis. Int J Diab Develop Count. 1994;14:74-82.
Kabadi UM. Pancreatic Ketoacidosis. A syndrome mimicking diabetic ketoacidosis. Endocr Pract. 2015;21(10):1184-1185. doi: https://doi.org/10.4158/1934-2403-21.10.1184.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


