Analysis of central axis and build up region dose calculated by different dose calculation algorithms used for radiation treatment planning
Abstract
Introduction: Computerized Treatment planning system (TPS) is an integral part of radiation treatment procedure. The main part of treatment planning system is a calculation algorithm incorporated in the Treatment Planning System. Various algorithms used in the TPS have capabilities and limitation on specific situations.
Objective: The objective of the work is to analyse the depth dose distribution generated by different dose calculation algorithms used in TPS in regions of low and high dose gradient.
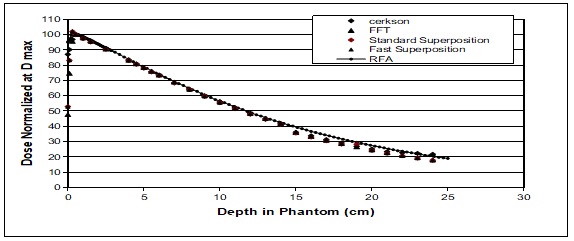
Materials and Methods: Four different dose calculation algorithms used for treatment planning such as Modified Clarkson, Sector integration, Fast Fourier Transform, Convolution- Superposition algorithm were used to generate the percentage depth dose distribution in a water phantom up to 25 cm depth. The values are compared with experimental results using Radiation Field Analyser. The PDD values also generated at build up region and the values were compared with experimental results using a Parallel plate ionization chamber.
Results: The results show that the dose calculated by different algorithms shows difference at build up region and at larger depths.
Downloads
References
Wen-Zhou Chen, Ying Xiao, Jun Li. Impact of dose calculation algorithm on radiation therapy World J Radiol. 2014;6(11):874-880. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i11.874.
Commissioning and quality assurance of computerized planning systems for radiation treatment of cancer. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna; 2004: Technical reports series No: 430.
Animesh. Advantages of multiple algorithm support in treatment planning system for external beam dose calculations J Can Res Ther. 2005;1(1):12-20. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.16085.
International Atomic Energy Agency. World Health Organization. Pan American Health Organization. European Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. IAEA. WHO. PAHO. ESTRO. Absorbed Dose Determination in External Beam Radiotherapy: An International Code of Practice for Dosimetry Based on Standard of Absorbed Dose to Water. International Atomic Energy Agency; 2000.
Fraass B, Doppke K, Hunt M, Kutcher G, Starkschall G et al. American association of physicists in medicine radiation therapy committee task group 53: Quality Assurance for Clinical Radiotherapy treatment planning. Med Phys. 1998;25(10):1773-1829. doi: https://doi.org/10.1118/1.598373.
Ahnesjö A, Knöös T, Montelius A. Application of the convolution method for calculation of output factors for therapy photon beams. Medical Phy. 1992;19(2):295-301. doi:10.1118/1.596859.
Oelkfe U., Scholz C. Dose Calculation Algorithms. In: Schlegel W., Bortfeld T., Grosu AL. (eds) New Technologies in Radiation Oncology. Medical Radiology (Radiation Oncology),2006. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-29999-8_15.
Rana S and Pokharel Verification of dose calculation algorithms in a multi-layer heterogeneous phantom using films. Gulf J Oncolog. 2013;1(14):63-69.
Miften M, Wiesmeyer M, Monthofer S, Krippner K. Implementation of FFT convolution and multigrid superposition models in the FOCUS RTP system Phys. Med. Biol. 2000;45(4):817-833. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/45/4/301.
Giraud CJ, Balosso J. Clinical Comparison of Pencil Beam Convolution and Clarkson Algorithms for Dose Calculation, J Cancer Ther. 2013;4(10):1485-1489. doi: 10.4236/jct.2013.410179.
Fotina, Kragl G, Kroupa B, Trausmuth R, Georg D. Clinical comparison of dose calculation using the enhanced collapsed cone algorithm vs. a new Monte Carlo algorithm. Strahlenther Onkol. 2011;187(7):433-441. doi: 10.1007/s00066-011-2215-9.
Kry SF, Alvarez P, Molineu A, Amador C, Galvin J, Followill DS. Algorithms used in heterogeneous dose calculations show systematic differences as measured with the radiological physics center’s anthropomorphic thorax phantom used for RTOG credentialing. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85(1):e95-e100. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.08.039.
Papanikolaou N, Stathakis S. Dose-calculation algorithms in the context of inhomogeneity corrections for high energy photon beams. Med Phys. 2009;36(10):4765-4767. doi:10.1118/1.3213523.
Knöös T, Wieslander E, Cozzi L, Brink C, Fogliata A, Albers D, et al. Comparison of dose calculation algorithms for treatment planning in external photon beam therapy for clinical situations. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(22):5785-807. doi::10.1088/0031-9155/51/22/005.
Kim YL, Suh TS, Ko SG, Lee JW. Comparison of Experimental and Radiation Therapy Planning (RTP) Dose Distributions on Air Cavity. J Radiol Sci Technol. 2010;33(3):261-268. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207232.
Kida S, Bal M, Kabus S, Negahdar M, Shan X, Loo Jr BW, et al, CT ventilation functional image-based IMRT treatment plans are comparable to SPECT ventilation functional image based plans, Radiother. Oncol. 118(3):521-527. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.02.019. Epub 2016 Feb 24.
Buzdar SA, Afzal M, Todd-Pokropek A. Comparison of pencil beam and collapsed cone algorithms, in radiotherapy treatment planning for 6 and 10 MV photon. Journal of Ayub Medical College Abbottabad. 2010;22(3):152-154.
Chaikh A, Khamphan C, Kumar T, Garcia R, Balosso J. What should we know about photon dose calculation algorithms used for radiotherapy? Their impact on dose distribution and medical decisions based on TCP/NTCP. Int J Cancer Ther Oncol. 2016;4(4):4418. doi: 10.14319/ijcto.44.18.
Chung H, Jin H, Dempsey JF, Liu C, Palta J, Suh TS et al. Evaluation of surface and build‐up region dose for intensity‐modulated radiation therapy in head and neck cancer. Med Phys. 2005;32(8):2682-2689 .doi 10.1118/1.1992067.
Gerbi BJ, Meigooni AS, Khan FM. Dose buildup for obliquely incident photon beams. Med Phys. 1987;14(3):393-399. doi 10.1118/1.596055.
Lamb A, Blake S. Investigation and modelling of the surface dose from linear accelerator produced 6 and 10 MV photon beams. Physics Med Biol. 1998;43(5):1133-1146. doi 10.1088/0031-9155/43/5/006.
Higgins PD., Han EY., Yuan JL, Hui S., Lee CK. Evaluation of surface and superficial dose for head and neck treatments using conventional or intensity-modulated techniques. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52(4):1135-1146. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/52/4/018.
Kesen ND, Akbas U, Koksal C, Bilge H. Investigation of AAA dose calculation algorithm accuracy in surface and buildup region for 6MV photon beam using markus parallel-plate ion chamber. J Xray Sci Technol. 2019;27(2):361-369. doi: 10.3233/XST-180489.
Bilge et. A H. Bilge, A. Çakır, M. Okutan, and H. Acar, Surface dose measurements with GafChromic EBT film for 6 and 18 MV photon beams, Physica Medica. 2009;25(2):101-104. doi: https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ejmp.2008.05.001.
Cao Y, Yang X, Yang Z, Qiu X, Lv Z, Lei M et.al. Superficial dose evaluation of four dose calculation algorithms, Radiat Phys Chem. 2017;137:23-28 : doi 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.02.032.
Kappas C, Rosenwald JC. Quality control of inhomogeneity correction algorithms used in treatment planning systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995;32(3):847-858. doi 10.1016/0360-3016(94)00474-Y
Van Dyk J, Barnett RB, Cygler JE, Shragge PC. Commissioning and quality assurance of treatment planning computers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993:26(2):261-273. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(93)90206-B


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


