Knowledge attitude and practice (KAP) of diabetes in Mathura Uttar Pradesh - An observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Objective of this study is to determine the knowledge, attitude and practice regarding type 2 diabetes in diabetics as well as in Non-diabetics and also to determine the knowledge versus practice gap among diabetics. There is almost no study of this kind from Uttar Pradesh region of India.
Material and method: A pretested and validated questionnaire were used for assessment of these parameters. This questionnaire was divided in to 3 parts. First part used for assessment of knowledge in all the study subjects and had 8 questions. Second part had five questions based on risk factors and complication of diabetes. Third part was used only for diabetics and again had five questions based on their health care seeking behavior. A total of 412 study subjects (206 diabetics and 206 Non-diabetics) were interviewed and their responses were noted in this questionnaire form.
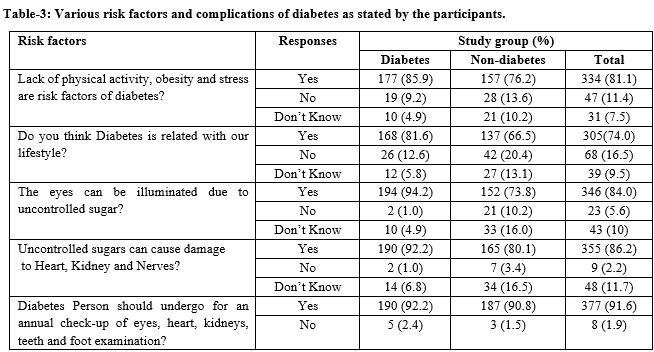
Results: 50% of the diabetics are in the age group category of 41-60 years. > 50% of non-diabetics are in the age group category 21-40 years. Most of the respondents were aware of symptomatology, non-communicability, need of self-monitoring of glucose at home and rapidly increasing incidence of diabetes. Almost 70 % of diabetics were aware about foot care and Very nominal number of diabetics (7.8%) was consuming sweets daily. A disheartening fact revealed that approximately 87% of diabetics do not carry sugar candy or any form of sugar before leaving home to correct any hypoglycemic episode.
Conclusion: Knowledge of symptomatology of diabetes and requirement of self-monitoring of blood glucose at home was adequate among most of the study subjects and uniformly distributed among diabetics and Nondiabetics. More than 80% of diabetics were not aware about hypoglycemia symptoms and its treatment. Training of health care providers and large-scale education and awareness campaigns are the need of the hour for this region to further improve the knowledge and to improve self-care practices among all Diabetics.
Downloads
References
Tham KY, Ong JJ, Tan DK, How KY. How much do diabetic patients know about diabetes mellitus and its complications? Annals-Acad Med Singapore. 2004;33(4):503-509.
Kaur K, Singh MM, Walia I. Knowledge and self-care practices of diabetics in a resettlement colony of Chandigarh. Ind J Med Sci. 1998;52(8):341-347.
Muninarayana C, Balachandra G, Hiremath SG, Iyengar K, Anil NS. Prevalence and awareness regarding diabetes mellitus in rural Tamaka, Kolar. Int J Diab Develop Count. 2010;30(1):18. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0973-3930.60005.
Mohan D, Raj D, Shanthirani CS, Datta M, Unwin NC, Kapur A, Mohan V. Awareness and knowledge of diabetes in Chennai-The Chennai urban rural epidemiology study [CURES-9]. JAPI. 2005;53:283-287.
Badruddin N, Basit A, Hydrie MZ, Hakeem R. Knowledge, attitude and practices of patients visiting a diabetes care unit. Pak J Nutri. 2002;1(2):99-102. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2002.99.102.
Saleh F, Mumu SJ, Ara F, Ali L, Hossain S, Ahmed KR. Knowledge, attitude and practice of type 2 diabetic patients regarding obesity: study in a tertiary care hospital in Bangladesh. J Pub Health Afr. 2012;3(1):e8. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4081%2Fjphia.2012.e8.
Saleh F, Mumu SJ, Ara F, Begum HA, Ali L. Knowledge and self-care practices regarding diabetes among newly diagnosed type 2 diabetics in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pub Health. 2012;12(1):1112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-12-1112.
Wee HL, Ho HK, Li SC. Public awareness of diabetes mellitus in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2002;43(3):128-134.
Fatema K, Hossain S, Natasha K, Chowdhury HA, Akter J, Khan T, Ali L. Knowledge attitude and practice regarding diabetes mellitus among Nondiabetic and diabetic study participants in Bangladesh. BMC Pub Health. 2017;17(1):364. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4285-9.
Raj CP, Angadi MM. Hospital-based KAP study on diabetes in Bijapur, Karnataka. Indian J Med Spec. 2010;1(2):80-83. doi:10.7713/ijms.2010.0022.
Al Shafaee MA, Al-Shukaili S, Rizvi SG, Al Farsi Y, Khan MA, Ganguly SS, et al. Knowledge and perceptions of diabetes in a semi-urban Omani population. BMC Pub Health. 2008;8(1):249. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-8-249.
Saeed NH. Diabetes-related knowledge, attitude, practice and beliefs among adult diabetic patients attending diabetic consultation clinic in Sulaimani city. Iraq: University of Sulaimani. 2009.
American Diabetes Association. Supplement 1. American Diabetes Association: clinical practice recommendations 2000. Diab Care. 2000;23(1):S1-116.
Goyder E, Irwig L. Screening for diabetes: what are we really doing? BMJ. 1998;317(7173):1644-1646. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.317.7173.1644.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


