The correlation of doxorubicin related cardiotoxicity with B-type natriuretic peptide levels in South Indian population
Abstract
Background: Anthracyclines represent the greatest risk for development of cardiotoxicity. Cardiotoxicity of anthracyclines may develop during the treatment (acute cardiotoxicity) and during the follow-up (chronic and late cardiotoxicity). Natriuretic peptides - Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP), B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP) are released by myocardium in response to wall strain and pressure overload. The applicability of natriuretic peptides (ANP, BNP, NT-pro-BNP) as markers for Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity has been investigated only in a few studies and there is scarcity of data from India.
Aims and Objectives: To observe correlation of NT-pro-BNP levels with cardiotoxicity in patients receiving doxorubicin.
Methods and Materials: Eighty patients who were planned for treatment with Doxorubicin > 200 mg/m2 were included in this study. Each patient was assessed clinically (History, Pulse rate, Blood pressure) along with ECG, ECHO and NT-pro-BNP levels prior to initiation of chemotherapy, after completion of 200 mg/m2 of Doxorubicin, 3 months and 6 months after chemotherapy.
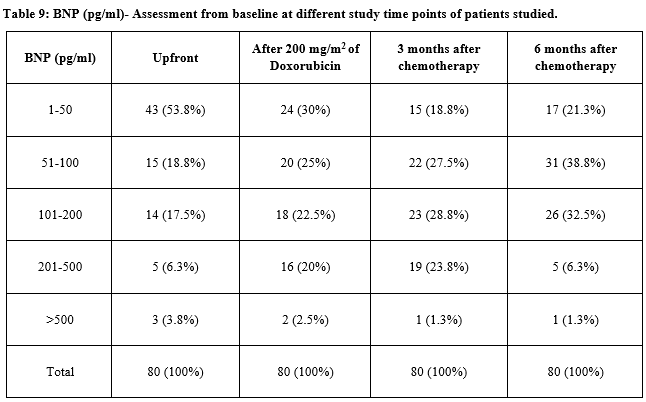
Result: There were total of 80 patients in the study and they received a total of 384 cycles of Doxorubicin containing regimens according to respective protocols. The median number of cycles was four (range four to six cycles). The mean cumulative dose of doxorubicin was 267.75 mg/m2. As none of the patients developed any cardiac symptoms during or after the planned chemotherapy nor was there a drop in Ejection Fraction on serial ECHO, correlation with BNP levels was not possible. There were 4 patients who had very high values of NT-pro-BNP (>300 pg/ml) and 4 patients with moderate elevation of NT-pro-BNP (200-300 pg/ml) prior to the initiation of chemotherapy. 14 patients had serially increasing values of NT-pro-BNP in the 6 months follow-up.
Conclusion: Based on the findings in this study it can be concluded that high upfront BNP values or increasing values of BNP does not correlate with the incidence of acute and early onset chronic cardiotoxicity. Whether or not the BNP values correlate with the incidence of late onset cardiotoxicity can be concluded only with a longer follow-up of these patients.
Downloads
References
Horacek JM, Pudil R, Jebavy L, Tichy M, Zak P, Maly J. Assessment of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity with biochemical markers. Exp Oncol. 2007;29(4):309-313.
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, et al. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulat. 2015;131(22):1981-1988. doi: https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013777. Epub 2015 May 6.
Adão R, de Keulenaer G, Leite-Moreira A, Brás-Silva C. Cardiotoxicity associated with cancer therapy: pathophysiology and prevention strategies. Rev Port Cardiol. 2013;32(5):395-409. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repce.2012.11.019 Epub 2013 Apr 24.
Eidem BW. Idenification of anthracycline cardiotoxicity: left ventricular ejection fraction is not enough. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21(12):1290-1292. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2008.10.008.
Rosner B, Fundamentals of Biostatistics, 5th Ed Duxbury:80-240.
Robert H, Statistics in Medicine, 2nd edition, Academic press:85-125.
Rao PS, Richard J. An Introduction to Biostatistics: A manual for students in health sciences. Prentice/Hall of India; 1996.
Suresh K.P., Chandrasekhar S, Sample Size estimation and Power analysis for Clinical research studies. J Human Reproduct Sci.2012. 5(1):7-13. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0974-1208.97779.
Hershman DL, Shao T. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity after breast cancer treatment. Oncol (Williston Park). 2009;23(3):227-234.
Sandri MT, Salvatici M, Cardinale D, Zorzino L, Passerini R, Lentati P, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide after high-dose chemotherapy: a marker predictive of cardiac dysfunction? Clin Chem. 2005; 51(8): 1405-1410. Epub 2005 Jun 2. doi: https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2005.050153.
Wang YD, Chen SX, Ren LQ. Serum B-type natriuretic peptide levels as a marker for anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Oncol Let. 2016;11(5):3483-3492.
Romano S, Fratini S, Ricevuto E, Procaccini V, Stifano G, Mancini M, et al. Serial measurements of NT-proBNP are predictive of not-high-dose anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Brit J Cancer. 2011; 105(11):1663-1668. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.439.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


