Evaluation of difficult airway in paediatric population ranging from 5-12 years age group
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to predict difficult airway on the basis of various airway assessment parameter in the paediatric population between 5-12 years age group. To assess the value of modified Mallampati test (MMT), upper-lip-bite test (ULBT), thyromental distance (TMD), ratio of height to thyromental distance (RHTMD) from which Cormack Lehane grade was derived to predict difficult airway i.e. difficult intubation in paediatric patients ranging from 5-12 years age.
Material and Methods: 100 ASA grade I & II paediatric patients of either sex between the age group of 5-12 years posted for elective surgery under general anaesthesia requiring endotracheal intubation were included in the study. Modified Mallampati test, upper lip bite test, thyromental distance and ratio of height to thyromental distance of the patients were measured and recorded. All the distances were measured with the help of a flexible measuring tape so as to measure the distances accurately.
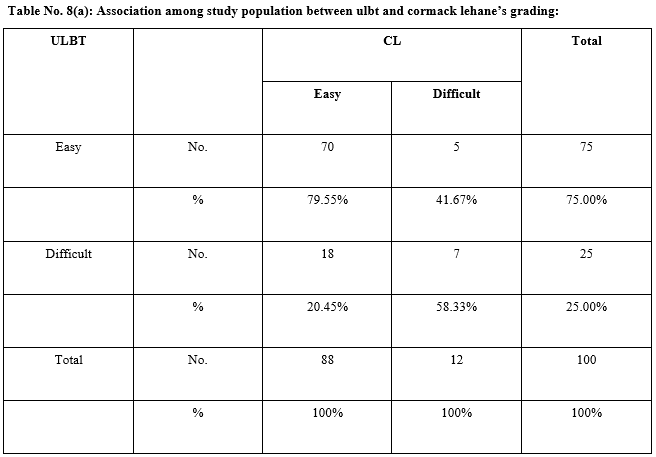
Results: Modified Mallampati test has the highest sensitivity (75%) and specificity (92.05%) among all the other screening tests. It also has high positive predictive value (56.25%), negative predictive value (96.43%) and diagnostic accuracy (90%). Upper Lip Bite test has high specificity (79.55%) and negative predictive value (93.33%) with high diagnostic accuracy (77%). It has a sensitivity of 58.33% which is similar to the sensitivity of thyromental distance and ratio of height to thyromental distance. Thyromental distance has high specificity (65.90%) with high negative predictive value (92.06%).
Conclusion: Modified Mallampati test is a useful bedside screening test for predicting difficult intubation in patients between 5-12 years age group. The Upper Lip bite test and thyromental distance has high specificity with high negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy. The ratio of height to thyromental distance is least useful predictor of airway assessment.
Downloads
References
Jain RR, Rabb MF. The difficult paediatric airway. In: Hageberg CA. Benumof and Hageberg’s Airway management. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2013. p. 723-60.
Ramachandran SK, Klock Jr PA. Definition and incidence of the difficult airway. InBenumof and Hagberg's airway management 2013: WB Saunders; pp. 201-208.
American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Management of the Difficult Airway. Practice guidelines for management of the difficult airway: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Management of the Difficult Airway. Anesthesiol. 2003;98(5):1269-1277. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200305000-00032
Larson SL, Jordan L. Preventable adverse patient outcomes: a closed claims analysis of respiratory incidents. AANA J. 2001;69(5):386-392.
Gupta S, Sharma R, Jain D. Airway assessment: predictors of difficult airway. Indian J Anaesth. 2005;49(4):257-262.
Rafique NB, Khan FA. Comparison of Mallampatti test, thyromental distance and distance from tragus to nares for predicting difficult intubation in pediatric patients. Open J Anesthesiol. 2014;4(04):104-109. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojanes.2014.44016.
Mallampati SR, Gatt SP, Gugino LD, Desai SP, Waraksa B, Freiberger D, et al. A clinical sign to predict difficult tracheal intubation: a prospective study. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1985;32(4):429-434. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03011357.
Khan ZH, Kashfi A, Ebrahimkhani E. A comparison of the upper lip bite test (a simple new technique) with modified Mallampati classification in predicting difficulty in endotracheal intubation: a prospective blinded study. Anesth Analg. 2003;96(2):595-599. doi: https://doi.org/10.1213/00000539-200302000-00053.
Salimi A, Farzanegan B, Rastegarpour A, Kolahi AA. Comparison of the upper lip bite test with measurement of thyromental distance for prediction of difficult intubations. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2008;46(2):61-65. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-4597(08)60027-2.
Krobbuaban B, Diregpoke S, Kumkeaw S, Tanomsat M. The predictive value of the height ratio and thyromental distance: four predictive tests for difficult laryngoscopy. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(5): 1542-1545. doi: https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000181000.43971.1E.
Eberhart LH, Arndt C, Cierpka T, Schwanekamp J, Wulf H, Putzke C. The reliability and validity of the upper lip bite test compared with the Mallampati classification to predict difficult laryngoscopy: an external prospective evaluation. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101(1):284-289.doi: https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000154535.33429.36.
Hester CE, Dietrich SA, White SW, Secrest JA, Lindgren KR, Smith T. A comparison of preoperative airway assessment techniques: the modified Mallampati and the upper lip bite test. AANA J. 2007;75(3):177-182.
Mehta T, Jayaprakash J, Shah V. Diagnostic value of different screening tests in isolation or combination for predicting difficult intubation: A prospective study. Indian journal of anaesthesia. 2014;58(6):754-757. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0019-5049.147176.
Karkouti K, Rose DK, Ferris LE, Wigglesworth DF, Meisami-Fard T, Lee H. Inter-observer reliability of ten tests used for predicting difficult tracheal intubation. Can J Anaesth. 1996;43(6):554-559. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03011765.
Schmitt HJ, Kirmse M, Radespiel-Troger M. Ratio of patient's height to thyromental distance improves prediction of difficult laryngoscopy. Anaesth Intensive Care.2002;30(6):763-765. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177%2F0310057X0203000607.
Cormack RS, Lehane J. Difficult tracheal intubation in obstetrics. Anaesthes. 1984;39(11):1105-1111. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb08932.x.
Savva D. Prediction of difficult tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73(2):149-153. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/73.2.149
Rucker JC, Cole D, Guerina LR, Zoran N, Chung F, Friedman Z. A prospective observational evaluation of an anatomically guided, logically formulated airway measure to predict difficult laryngoscopy. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2012; 29(5):213-217. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0b013e3283502168.
Adamus M, Fritscherova S, Hrabalek L, Gabrhelik T, Zapletalova J, Janout V. Mallampati test as a predi-ctor of laryngoscopic view. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2010;154(4):339-343.
Kim WH, Ahn HJ, Lee CJ, Shin BS, Ko JS, Choi SJ, et al. Neck circumference to thyromental distance ratio: a new predictor of difficult intubation in obese patients. Br J Anaesth. 2011;106(5):743-748. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aer024. Epub 2011 Feb 24.
Cheney FW, Posner KL, Lee LA, Caplan RA, Domino KB. Trends in anesthesia-related death and brain damage: A closed claims analysis. Anesthesiol. 2006;105(6):1081-1086. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200612000-00007.
Aggarwal A, Sharma KR, Verma UC. Evaluation of difficult Airway predictors in pediatric population as a clinical investigation. J Anesth Clin Res. 2012;3(11):1-5. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2155-6148.1000256.
Inal MT, Memiş D, Sahin SH, Gunday I. [Comparison of different tests to determine difficult intubation in pediatric patients]. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2014;64(6):391-394. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjane.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Aug 28.
Valley RD, Freid EB, Bailey AG, Kopp VJ, Georges LS, Fletcher J, et al. Tracheal extubation of deeply anesthetized pediatric patients: a comparison of desflurane and sevoflurane. Anesth Analg. 2003;96(5): 1320-1324. doi: https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000058844.77403.16.
Salimi A, Farzanegan B, Rastegarpour A, Kolahi AA. Comparison of the upper lip bite test with measurement of thyromental distance for prediction of difficult intubations.Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2008;46 (2):61-65.doi:10.1016/S1875-4597(08)60027-2.
Brodsky JB, Lemmens HJ, Brock-Utne JG, Vierra M, Saidman LJ. Morbid obesity and tracheal intubation. Anesth Analg. 2002;94(3):732-736. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000539-200203000-00047.
Safavi M, Honarmand A, Zare N. A comparison of the ratio of patient's height to thyromental distance with the modified Mallampati and the upper lip bite test in predicting difficult laryngoscopy. Saudi J Anaesth. 2011;5(3):258-263. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F1658-354X.84098.
Krobbuaban B, Diregpoke S, Kumkeaw S, Tanomsat M. The predictive value of the height ratio and thyromental distance: four predictive tests for difficult laryngoscopy. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(5): 1542-1545.doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000181000.43971. 1E
Khan RM. Airway management. 6th ed. Hyderabad: Paras medical publisher; 2018.
Ayoub C, Baraka A, el-Khatib M, Muallem M, Kawkabani N, Soueide A. A new cut-off point of thyromental distance for prediction of difficult airway. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2000;15(6):619-633.
Frerk CM. Predicting difficult intubation. Anaesthesia.1991;46(12):1005-1008.doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1991.tb09909.x.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


