A study of demographic profile of HIV positive patients attending ART centre SGMH Rewa, Madhya Pradesh
Abstract
Background: Caused by Human Immuno-deficiency virus, leading the patient’s immune system vulnerable to various infections and neurological disorder, AIDS have transformed into a socioeconomic and developmental concern. With the increasing population of India, the HIV epidemic will soon be a major cause of concern. The objective of the present study was to observe the demographic profile of HIV positive patients attending ART Centre at the Department of Medicine at Sanjay Gandhi Memorial Hospital & Shyam Shah Medical College, Rewa (M.P.) in year 2012-2014.
Material & Methods: This was a data-based study. In this study total 1224 cases of all age group were taken, these patients were registered in ART center in between Jan. 2010 to Dec.2012. A pre-formed questionnaire (proforma) was made to enquire about socio-demographic-economic variables. The patient and their spouse were interviewed, examined and investigated according to pre-designed proforma with special reference to their occupation, spouse HIV status and high-risk behaviour.
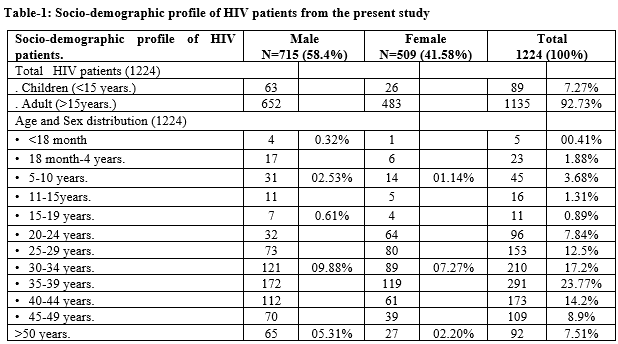
Results: In this study total number of ART attendees (patients) were 1224 and out of these total patients, 7.27% (n=89) were children (<15years) and 92.73% (n=1135) were adult (>15 years). Out of 89 children, 5.15% (n=63) were male and 2.12% (n=26) were female and out of 1135 adult patients, 53.26% (n=652) were male and 39.46% (n=483) were female. M/F ratio in children was 2.4/1 and M/F ratio in adult patients was 1.3/1.
Conclusion: As the present study was done in rural area, where hygiene was poor and sanitation was bad and environment was dusty, that is why infectious complications were more common in the present study.
Downloads
References
AIDS Epidemic Update. WHO/UNAIDS, December 2010 report Available at http://www.unaids.org/en/HIV.data Accessed on 26 August 2019.
AIDS-life positive. Available on http://www.lifepositive.com/aids. Accessed on 30 July 2019.
AIDS Epidemic Update. WHO/UNAIDS, November 2012-13 report Available at http://www.unaids.org/en/HIV.data Accessed on 13 August 2019.
Park K. Park’s Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine. 22th.ed Jabalpur (India): M/s Banarsidas Bhanot; 2011;316-319.
Umesh S. Joge, Deepali S. Dev, and Rajesh N. Lakde et al. Socio-demographic and clinical profile of HIV/AIDS patient visiting to ART center at a rural tertiary care hospital in Maharashtra state of India. Int J Bio Med Res 2012;3(2):1568-1572.
The History of HIV/AIDS in India, available on http://www.aidsdatahub.org/dmdocument/HIV_AIDS_in_Indiapdf. Accessed on 15 June 2019.
Simoes EA, Babu PG, John TJ, Nirmala S, Solomon S, Lakshmi N et al. Evidence for HTLV-III infection in prostitutes in Tamil Nadu (India). Indian J Med Res. 1987;85:335-338.
NACO (2003) HIV/AIDS Surveillance in India. Available from: http://www.avert.org/aidsindia.htm Accessed on 2 August 2019.
Lal S. Surveillance of HIV/AIDS in India (Editorial). Indian J Comm Med. 2003;(1):3-9.
An Overview of the Spread and Prevalence of HIV/AIDS in India. Available from website: http://www.naco.nic.in/nacp/bss1.pdf. Accessed on 7 August 2019.
National AIDS Control Organization. Combating HIV/AIDS in India, 1999-2000. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
“Now commercial capital of M.P (Indore) become the capital of AIDS”./’Number of aids cases is increasing in M.p and Indore remained the city with most number of AIDS cases in M.P’. Articles available on. http://www.mpsacsb.org/programmes.html Accessed on June 13, 2019.
NACO (2003) HIV/AIDS Surveillance in India. Available from: http://www.avert.org/aidsindia.htm Accessed on 13 June 2019.
172,000 people died of AIDS in India/According to the NACO HIV/AIDS cases in India are declining as per new estimates. India Fact Health, 2012.
Combating HIV/AIDS in India 19992000.Voluntary Counseling and Testing, New Delhi, In India. National AIDS control organization (NACO), ministry of health and welfare, Government India;19992000;12:70-74.
Campbell JC, Marum ME, Alwano-Edyegu M, Dillon BA, Moore M, Gumisiriza E. The role of HIV counseling and testing in the developing world. AIDS education and prevention: official publication of the Int Soc AIDS Educat. 1997;9(3 Suppl):92-104.
UNAIDS report 2012 on the global AIDS epidemic. available on, http://www.unaidsorg/en/media/unaids/contentstassets/document/epidemiology2012_UNAIDS_Global_Report_2012. Accessed on 25 July 2019.
NACO HIV/AIDS Report June 2012-13 Available on 'http://www.nacoonline.org/NACO. Accessed on June 17, 2013
Sonani HP, Unghad AK, Savani GT. Clinical and demographic profile of patient registered at ART centre Smimer, Surat. Nat J Comm Med. 2011;2(1):130-132.
NACO (2005), ‘UNGASS India report: progress report on the declaration of commitment on HIV/AIDS’. Accessed on 18 July 2019
Population statistics of Madhya Pradesh. Available on India: Madhya Pradesh http://www.citypopulation.de/india-MadhyaPradesh./htm/2011-03-01 Accessed on 4 July 2019.
Madhya Pradesh sex ratio available on http://www/mapsofindia.com.census2011madhyapredesh-sex.ratio.htm/ Accessed on 4 June 2019.
Wani KA. Clinical profile of HIV/AIDS patients in Srinagar, Kashmir, India. Int J Collab Res Intern Med Public Health. 2012;4:1703-1712
Uma T, Srijayanth P, Valarmathi S, Sekar S, Kabilan N, Natarajan M. Socio-demographic profile of HIV/AIDS patients at ART centres in Chennai. BMC infectious diseases. 2012 Dec 1;12(S1):P53. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-12-S1-P53.
Chakravarty J, Mehta H, Parekh A, Attili SV, Agrawal NR, Singh SP et al. Study on Clinicoepidemiological profile of HIV patients in Eastern India. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006;54:854-857.
Rajasekaran S, Jeyaseelan L, Raja K, Ravichandran N. Demographic & clinical profile of HIV infected children accessing care at Tambaram, Chennai, India. Indian J Med Res. 2009;129(1):42-49.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


