Glycemic control amongst diabetic subjects on insulin therapy: Still off target!
Abstract
Introduction: Prevalence of diabetes is increasing worldwide. Good glycemic control is essential for prevention of complications of diabetes. Despite of availability of multiple medications, it is difficult to achieve good glycemic control. Insulin therapy is considered to be the best option available for attaining glycemic control. But, whether insulin therapy has achieved it is an important question to be addressed.
Objective: To assess the glycemic control in subjects with diabetes on insulin therapy.
Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was done at Karnataka Institute of Endocrinology and research, Bangalore, in 448 diabetic patients who were on insulin therapy as a part of their diabetic therapy. Data collected was analyzed using SPSS 22 version software.
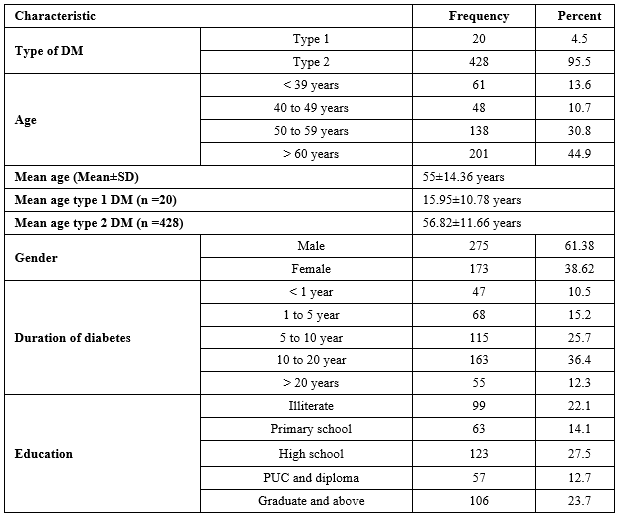
Results: Majority of the subjects were men (61.38%) and in the age group of > 60 years (44.9%). Many of the subjects on insulin therapy had duration of diabetes > 5 years, with 36.4% having duration of 10-20 years, while another 36% had duration of 5 -10 years. Premixed insulin (81.47%) was the most commonly used insulin regimen. 82.6% of the subjects were on conventional insulin and only 13.2% were on insulin analogues. Insulin syringe was the most commonly used delivery device, with 64.7% of subjects using it, while insulin pen was used by 33.5% subjects. Despite of insulin therapy, the glycemic control was poor and 81.4% had HbA1c >8%. Only 5.7% of the subjects had HbA1c <7%. 94.9% of the subjects reported that they were regular with their insulin therapy. Only 20.1% adjusted the insulin dose by self.
Conclusions: The present study has found that despite being on insulin therapy, large percentage of subjects was unable to achieve good glycemic control.
Downloads
References
Federation ID. IDF Diabetes Atlas Eighth Edition 2017.
World Health Organization. Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013-2020.
Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR.Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA. 1999;281(21):2005-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.281.21.2005
Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diab Care. 2009;32(1):193-203. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-9025. Epub 2008 Oct 22.
Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Khunti K. Addressing barriers to initiation of insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(1):S11-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1751-9918(10)60004-6.
American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diab Care. 2019;42(1):S61-S70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S006.
Resnick HE, Foster GL, Bardsley J, Ratner RE. Achievement of American Diabetes Association clinical practice recommendations among U.S. adults with diabetes, 1999-2002: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diab Care. 2006;29(3):531-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.29.03.06.dc05-1254
Siddiqui FJ, Avan BI, Mahmud S, Nanan DJ, Jabbar A, Assam PN. Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus: prevalence and risk factors among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in an Urban District of Karachi, Pakistan. Diab Res Clin Pract. 2015;107(1):148-56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.09.025. Epub 2014 Oct 5.
Fiagbe J, Bosoka S, Opong J, Takramah W, Axame WK, Owusu R, et al. Prevalence of controlled and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and associated factors of controlled diabetes among diabetic adults in the hohoe municipality of Ghana. Diab Manage.2017; 7(5):343-54
Navarro-Vidal B, Banegas JR, León-Muñoz LM, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, Graciani A. Achievement of cardiometabolic goals among diabetic patients in Spain. A nationwide population-based study. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61549.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061549. Print 2013.
Raheja BS, Kapur A, Bhoraskar A, Sathe SR, Jorgensen LN, Moorthi SR, et al. DiabCare Asia--India Study: diabetes care in India--current status. J Assoc Physicians India. 2001;49:717-22.
Mohan V, Shah SN, Joshi SR, Seshiah V, Sahay BK, Banerjee S, et al. Current status of management, control, complications and psychosocial aspects of patients with diabetes in India: Results from the Diab CareIndia2011Study.Indian JEndocrinolMetab. 2014;18 (3):370-8.DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F2230-8210.129715.
Goyal J, Kumar N, Sharma M, Raghav MS, Lal B, Bhatia PS. Factors affecting glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes at a tertiary health care center of western UP region: a cross-sectional study. Int J Health Sci Res. 2019; 9(3):12-20.
Alzaheb RA, Altemani AH. The prevalence and determinants of poor glycemic control among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018; 11:15-21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S156214. eCollection 2018.
Viana LV, Leitão CB, Kramer CK, Zucatti AT, Jezini DL, Felício J, et al. Poor glycaemic control in Brazilian patients with type 2 diabetes attending the public healthcare system: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2013;3 (9):e003336. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003336.
Alramadan MJ, Magliano DJ, Almigbal TH, Batais MA, Afroz A, Alramadhan HJ, et al. Glycaemic control for people with type 2 diabetes in Saudi Arabia - an urgent need for a review of management plan. BMC Endocr Disord. 2018;18(1):62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-018-0292-9.
Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM, Deepa M, Pradeepa R, Joshi SR, Bhansali A, et al. Glycemic control among individuals with self-reported diabetes in India--the ICMR-INDIAB Study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014; 16 (9): 596-603. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2014.0018. Epub 2014 Aug 7.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


