A study on incidence of subclinical hypothyriodism in patients with heart failure
Abstract
Objectives: Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is a common disorder that is characterized by elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone levels in conjunction with free thyroxine concentrations within the normal reference range. Thyroid hormones are known to affect the heart and vasculature and, as a result, the impact of SCH on heart failure. Strong evidence points to a link between SCH and HF risk factors such as alterations in blood pressure, lipid levels, and atherosclerosis. Additionally, accumulating evidence indicates that SCH is associated with metabolic syndrome and heart failure. The present review proposes that SCH may be a potentially modifiable risk factor of heart failure and mortality.
Methods: This is an observational study to determine the incidence of subclinical hypothyroidism in patients with heart failure and the cardiovascular risk profile among patients in a 750 bedded tertiary health care centre in south India, over a period from June 2018 to November 2018.
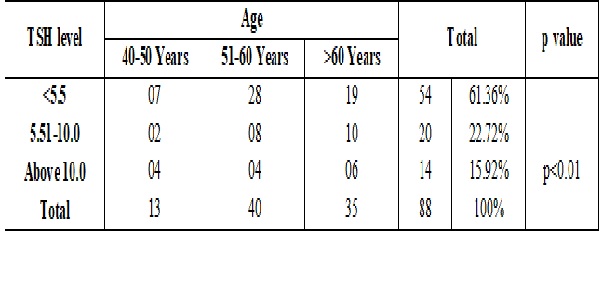
Results: In our present study it was noticed that most of the patients were in the age group above 51-60 yrs (45.45 %). Our study data suggest that subclinical hypothyroidism with a TSH ≥10.0 mIU/L represents a potentially modifiable risk factor for HF in older adults but not subclinical hypothyroidism with moderate TSH levels (TSH 4.5 to 9.9 mIU/L) and subclinical hyperthyroidism.
Conclusion: Subclinical hypothyroidism are more prone to associated with heart failure as an asymptomatic which is essential to be identified and treated for a better outcome as its association is proven statistically in our study.
Downloads
References
Klein I, Danzi S. Thyroid disease and the heart. Circulation. 2007 Oct 9;116(15):1725-35.
Ochs N, Auer R, Bauer DC, et al. Meta-analysis: subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk for coronary heart disease and mortality. Ann Intern Med. 2008 Jun 3;148(11):832-45. Epub 2008 May 19.
Razvi S, Shakoor A, Vanderpump M, et al. The influence of age on the relationship between subclinical hypothyroidism and ischemic heart disease: a metaanalysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Aug;93(8):2998-3007. doi: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0167.
Pearce SH, Brabant G, Duntas LH, et al. 2013 ETA Guideline: Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism. Eur Thyroid J. 2013 Dec;2(4):215-28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000356507. Epub 2013 Nov 27.
Kahaly GJ, Dillmann WH. Thyroid hormone action in the heart. Endocr Rev. 2005 Aug;26(5):704-28. Epub 2005 Jan 4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2003-0033.
Rodondi N, Bauer DC, Cappola AR, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction, cardiac function, and the risk of heart failure. The Cardiovascular Health study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Sep 30;52(14):1152-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.009.
Iervasi G, Pingitore A, Landi P, et al. Low-T3 syndrome: a strong prognostic predictor of death in patients with heart disease. Circulation. 2003 Feb 11;107(5):708-13.
Cooper DS, Biondi B. Subclinical thyroid disease. Lancet. 2012 Mar 24;379(9821):1142-54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60276-6.
Bastenie PA, Vanhaelst L, Neve P. Coronary-artery disease in hypothyroidism. Lancet. 1967 Dec 9;2(7528):1221-2.
Pittman JA Jr, Dailey GE 3rd, Beschi RJ. Changing normal values for thyroidal radioiodine uptake. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 26;280(26):1431-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196906262802602
Bastenie PA, Banhaelst L, Bonny M, Neve P, Staquet M, 1971: Preclincal hypothyroidism a risk factor for coronary heart disease, Lancet 1:203-204.
Zondek AJ. Kamilton EA. Heart and hypothyroidism Arch Intern Med 1918;53-65.
Wang R, Nelson JC, Weiss RM, et al. Accuracy of free thyroxine measurements across natural ranges of thyroxine binding to serum proteins. Thyroid. 2000 Jan;10(1):31-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2000.10.31
Monzani F, Caraccio N, Del Guerra P, Casolaro A, Ferrannini E 1999Neuromuscular symptoms and dysfunction in subclinical hypothyroid patients: beneficial effect of L-T4 replacement therapy. Clin Endocrinol 51:237–242.
Kahaly GJ. Cardiovascular and atherogenic aspects of subclinical hypothyroidism. Thyroid. 2000 Aug;10(8):665-79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/10507250050137743


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


