Perceptions and Suggestions of II year M.B.B.S. Students Regarding Updated Pathology Teaching Curriculum: An Analytic Study
Abstract
Introduction: In most of the medical colleges of India, the knowledge regarding basic science subjects is taught mainly through didactic lectures, tutorials and practicals. And hence the system is more of teacher centered with less interaction or involvement from the students. There is a need to explore innovations, so as to sustain interest.
Objectives: To introduce interactive teaching and assessment methods during lectures and examinations respectively and to elicit student’s perception about them.
Materials and Method: A number of interactive methods were introduced in the pathology curriculum in a batch of 153 medical students of 2nd year M.B.B.S. Later the perceptions of the students were elicited regarding these sessions using a questionnaire based on Likert scale.
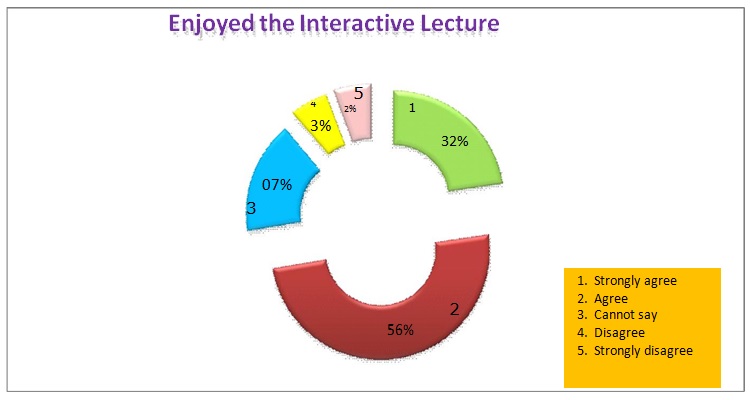
Results: Validation of the scale indicated good internal consistency with Crohnbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.9. Majority (83%) of the students agreed or strongly agreed to like the interactive sessions. Similarly, 86% agreed or strongly agreed to like teamwork in group discussions and quiz sessions. Most popular interactive mode was MCQ’s followed by Cinemeducation. Most students were also of the view that interactivity during lectures keeps them active, more attentive in the class, makes the atmosphere more lively, also improved their communication skills, helps in retention of the topic, clearing doubts, improves attention span and hence results in better understanding of the subject.
Conclusion: This project clearly proves that updated pathology curriculum is preferred by students. So, teacher should take a new role of facilitating the process of interactive learning rather than delivering elaborative lectures.
Downloads
References
Shah AR, Shethwala ND, Parmar BH. Perception of undergraduate medical students towards the subject of pathology at one of the medical colleges of Gujarat, India. International Journal of Medical Science and Public Health 2014; 3(7):863-865.
Mohamed EL-Bab Fath EL-Bab, Bassem Sheikh, Sherin Shalaby, Mohamed EL-Awady, Abbas Allam. Evaluation of Basic medical sciences knowledge retention among medical students. Ibnosina Journal of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. 2011 ;3(1): 45– 52.
Vanishree BJ, Nayaka R, Manjunath S. Somannavar, Sonoli SS. The perception of MBBS interns towards biochemistry Curriculum in a south Indian Medical College. NJIRM 2016; 7(4): 82-86.
Arachana C Buch, Chandanwala S.S. Bamnikar SA. Interactive teaching: Understanding perspectives of II MBBS students in Pathology. Medical Journal of D.Y. Pat University. Nov- Dec 2014;7(6): 693-695.
Borkar RS, Meshram SA, Jadhav PE. Introducing interactivity in community medicine classes for arousing interest in the subject amongst IInd. MBBS students. Res Anal Eval 2012;4:47-8.
Kate MS, Kulkarni UJ, Supe A, Deshmukh YA. Introducing integrated teaching in undergraduate medical curriculum. International Journal of Pharma Sciences and Research. 2010;1(1):18-22.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


