A study to assess the selfitis behaviour and selfie syndrome (level of selfitis) among the nursing students
Abstract
Background: Photography is seen as a powerful means of expression, as a symbolic language to express what cannot be said in words, and as a stimulator of emotions and behaviors about which often are not aware. The term the word "selfie", is declared as the "word of the year" by the Oxford English Dictionary. Selfie fever has taken a new dimension known as ‘selfitis’.
Objectives: To assess the selfitis behavior, the selfie syndrome (level of selfitis) and find out significant association of selected background variables with selfie syndrome (level of selfitis) among nursing students.
Material and Methods: It is a non-experimental study carried out on the nursing students in nursing training institutes in Bikaner city, Rajasthan. A study was conducted during the year of 2018 and 200 nursing students who are under training of GNM, B.Sc. nursing and M.Sc. Nursing were selected by using multi stage random sampling. Self developed questionnaire, Selfitis behavior scale and structured questionnaire used to collect the date from participants.
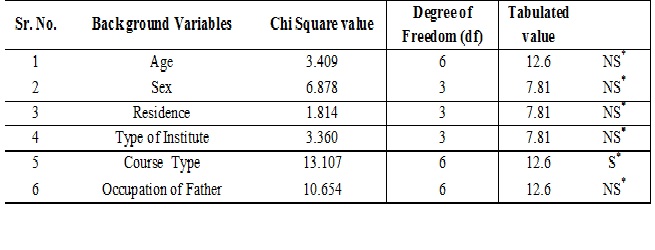
Results: Based on the finding of the majority of 141(70.5%) nursing students has moderate selfitis behavior followed by 59(29.50%) nursing students has severe Selfitis Behaviour and no candidate has mild Selfitis. The mean score of selfitis behaviour was 62.595 with SD 12.334. Based on findings there was no significant association of back ground variable with the level of selfitis except type of course in which student is admitted for nursing training.
Conclusion: The present study has proved that selfie syndrome is dominantly developing craze of modern era due to modern fat changes in technologies. From the finding of the present study it is concluded that the majority of nursing students have moderate selfitis behaviour.
Downloads
References
Psychological study project The Psychologically Beneficial Aspects of Photography, Adam Natoli, Dr. John Suler in Psychology Department of Rider University 2011available at https://www.truecenterpublishing.com
Katz J.E. and Crocker E.T. Selfies and photo messaging as visual conversation: Reports from the United States, United Kingdom and China. International Journal of Communication, 9 (2015), (1861-1872. 1932-8036/2015FEA0002.
Veena. G: Perception towards capturing selfies and its impact among students of Mangalore University: A Study International Journal of Digital Library Services Online available on https://www.ijodls
Albury K. (2015). Selfies, sexts, and sneaky hats: Young people’s understandings of gendered practices of selfie presentation. International Journal of Communication, 9,1734-1745.
Vats M, Selfie syndrome: An Infectious Gift of IT to Health Care. J Lung Pulm Respirres. 2015;2 (4):48.
Satish Saroshe, Ruchita Banseria et al: Assessment of Selfie Syndrome among the Professional Students of a Cosmopolitan City of Central India: A Cross-sectional Study Int J Ment Health Addiction https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-017-9844-x
Bhardwaj. A, Avasthi. V, Goundar. S; Impact of Social Net working on Indian Youth-A Survey, International Journal of Electronics and Information Engineering; Vol.7PP 41-51, Sep.2017( DOI:10.6636/ IJEIE.201709.7 (1).05) 41; available. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322538324.
Thakur N, Gaikwad Dagdu A., Assess the Selfie Taking Behaviour and its Impact on the Health of late Adolescents with a view to Develop Awareness Program for selected University of Gurugram, Haryana, International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), ISSN (Online):2319-7064, impact factor (20170:296).
Kela R, Khan N, Saraswat R, Amin B. Selfie: Enjoyment and Addiction, JMSCR January; 05(1):15836-15840.
Mrs. Sonalika. S.; An exploratory study to assess the knowledge regarding Selfitis among Adolescents in colleges of Bhubaneswar, International Journal of Advances in Nursing Management, volume no:6, issue no. 1 ISSN Print: 2347-8632, ISSN Online:2454-2652.
Kaur Sukhdeep & Maheswari SK Conduct a study Narcissistic personality and selfie taking behavior among college students, International Journal of Medical and Health research, ISSN:2454-9142, Impact Factor:RJIF5.54,Volume 4, Issue 5; May 2018,Page no. 56-60 available at https://medicalsciencejournal.com


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


