Knowledge and Awareness of the usage of Artificial Sweeteners among Indian type 2 diabetes individuals in a tertiary diabetes institute
Shetty S.1*, Anil Kumar R.2, R S.3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2022.i05.01
1* Sharanya S Shetty, Dietitian, Karnataka Institute of Endocrinology and Research, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
2 R Anil Kumar, Associate professor and HOD, Karnataka Institute of Endocrinology and Research, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
3 Shruthi R, Dietitian, Karnataka Institute of Endocrinology and Research, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India.
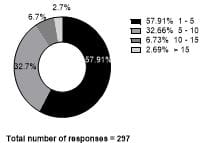
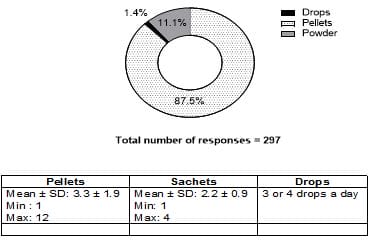
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease primarily attributable to unhealthy, untimely food habits and lack of physical activity. Good glycemic control is one of key aspects of preventing complications. This has led to shift in replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners amongst diabetic population. It is not known whether this is aimed to maintain blood glucose levels or satisfying sweet cravings. There is lack of awareness of type and long-term side effects of artificial sweeteners among people with diabetes. Objectives: This study was conducted to assess awareness and knowledge of usage of artificial sweeteners among adults with type 2 diabetes visiting a tertiary diabetes institute. Materials and Methods: The study population involved 297 adults (≥18 years) with type 2 diabetes attending a tertiary diabetes institute. Data were collected from face-to-face interview techniques along with pre-validated questionnaire. Results: The total number of subjects (n=297) comprised 126 females and 171 males of age 18-88 with a mean age of 56.5 years. Sucralose was most popular sugar substitute amongst the subjects (45%) followed by Aspartame (32%), 13% of them are completely not aware of type of artificial sweetener that they consumed. About 36.7% of subjects belonged to pre-obese category with a BMI of 25-29.9kg/m2 with women on the upper scale. 57.91% of the respondents started consuming artificial sweeteners in recent years i.e., between 1to 5 years. 87% of the subjects consumed artificial sweeteners in form of pellets in tea or coffee as medium and 51% consumed it to manage blood glucose levels. 51.2% had gastrointestinal side effects. A significant number of subjects (81.5%) were unaware of long-term side effects of artificial sweeteners. Conclusions: The study findings highlight high rate of unawareness amongst subjects regarding the side effects of long-term consumption of artificial sweeteners. Hence, reading nutrition label on products, judicious consumption of artificial sweeteners and nutritional education can help make wise food choices.
Keywords: Knowledge and Awareness, Artificial Sweeteners, type 2 diabetes
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Dietitian, , Karnataka Institute of Endocrinology and Research, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. Email: |
Sharanya S Shetty, R Anil Kumar, Shruthi R, Knowledge and Awareness of the usage of Artificial Sweeteners among Indian type 2 diabetes individuals in a tertiary diabetes institute. Int J Med Res Rev. 2022;10(5):134-140. Available From https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/1396 |


 ©
© 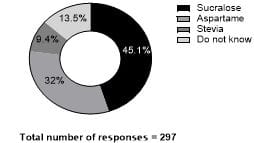 Figure 2: Distribution of type of artificial sweeteners consumed
Figure 2: Distribution of type of artificial sweeteners consumed