Clinical Spectrum and Management of hydatidosis – A Prospective Study
Pandey S.1, Kumar Shukla R.2, Chawla K.3, Mishra A.4*
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2021.i05.04
1 Sanjay Pandey, Senior Consultant, Department of Surgery, District Female Hospital, Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
2 Rakesh Kumar Shukla, Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Autonomous State Medical College and Hospital, Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
3 Kavita Chawla, Professor, Department of Physiology, Moti Lal Nehru Medical College, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, India.
4* Archana Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Biochemistry, Moti Lal Nehru Medical College, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, India.
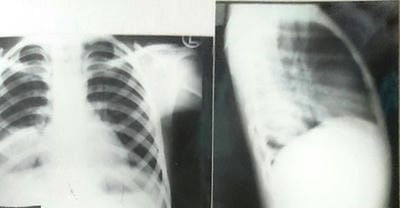
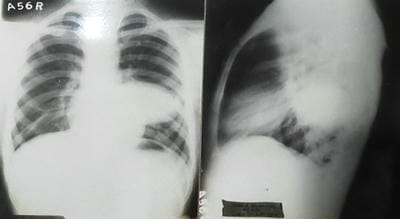
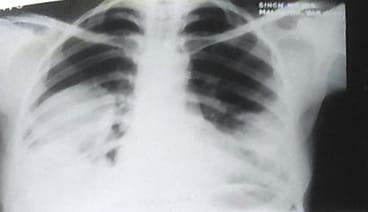
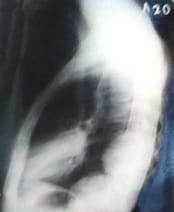
Aim: The objective of this original research article is a Clinical Spectrum and Management of hydatidosis – A Prospective Study. Material & method: -The present study includes 150 patients with intrathoracic space-occupying lesions, of which 24 patients with Hydatid cyst were seen at SS hospital Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, UP. Most of the patients studied were from the thoracic surgery section, while few patients were taken from other departments of SS hospital. The age of those patients varied widely, starting from 10 years to 60 years. During this study, patients were investigated in systemic order with the progression of symptoms from the onset, development of latest symptoms and treatment taken before if any, history of tuberculosis, chronic cough, smoking, and contact with were recorded. The patient's vitals were recorded, and routine pathological investigation including blood count, hemoglobin and specific procedure like radiological method, Casoni diagnostic test and bronchoscopy were performed. Result: Maximum patients were in the age group of 41 to 50 years. The maximum age group was 60 years, and the minimum age group was ten years. Maximum age group 21-30 years, among which this has been observed. No cases were seen above 41 years of age. Hemoglobin was found adequate among the cases. Total Leucocytes count was found higher among the patients. In 63% cases, found above 10000 per microliter. ESR found raised among the patients and in 50% of cases observed more than 40 mm in 1st hour. Cough with/without expectoration, Chest pain, and Dyspnoea were observed in almost all cases. The right side of the Lung had 50% involvement; the Left side of the Lung had 37.5% involvement, whereas 12.5% bilateral involvement. Conclusion: Mini-thoracotomy is an efficient and safe option for managing intact or ruptured solitary pulmonary hydatid cysts.
Keywords: Multiple hydatid cysts, Hydatid Cyst, Hydatidosis, Mini – Thoracotomy
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Biochemistry, Moti Lal Nehru Medical College, Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, India. Email: |
Sanjay Pandey, Rakesh Kumar Shukla, Kavita Chawla, Archana Mishra, Clinical Spectrum and Management of hydatidosis – A Prospective Study. Int J Med Res Rev. 2021;9(5):298-305. Available From https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/1334 |


 ©
©