Analysis of D-Dimer Levels among Covid -19 Positive Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangalore
Manasa S.1*, Vikram. H. C V.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2021.i02.05
1* Manasa S, Microbiologist, Sagar hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
2 Venkatesh Vikram. H. C, Medical Director, Sagar hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
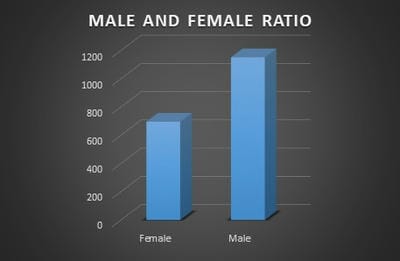
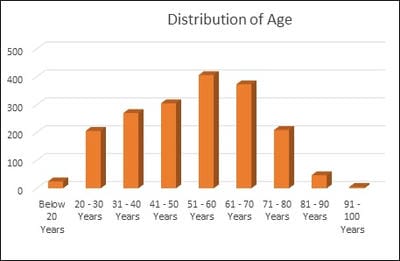
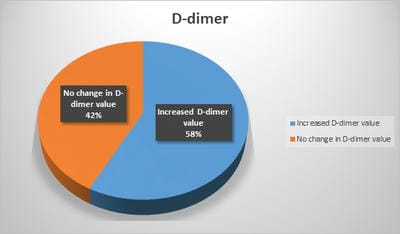
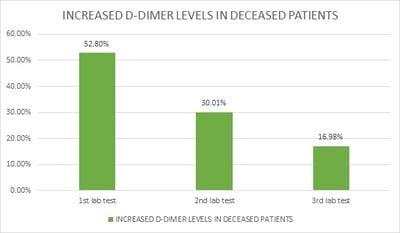
Introduction: Pro-thrombotic changes are stimulated by Corona Virus as it has an affinity for endothelium and lung structures and this may explain its association with thrombotic events, reduction of pulmonary gas exchange, respiratory distress, and death. D-dimer is a specific marker of the breakdown of a fibrin clot and has been used as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in VTE and other coagulation disorders. Objectives: The objective of this study was to assess the correlation of the D-Dimer levels and disease severity among COVID-19 patients. Materials and methods: This is a retrospective study done over 6 months from July 2020 to December 2020 in a tertiary care hospital in Bangalore. All the COVID- 19 positive cases who were admitted to our hospital were audited regarding the D-dimer levels during admission and the course of the treatment. Results: Coagulation disorder occurred at the early stage of COVID-19 infection, with 1066 (57.7%) patients having increased D-dimer levels. Out of 1846 COVID 19 patients 106 (5.7%)patients died due to complications. 106 patients who deceased, all the patients had an increased D dimer value either in the first lab test or in the consecutive tests. Among 106 patients 56(52.8%) patients had increased D-dimer at the first lab test, 32 (30.1%) had D-dimer increased at the second and 18(16.98%) in third lab tests. The increased D-dimer levels were closely associated with the progression of the disease and also the changes in the CT imaging. Conclusion: The increase in D-Dimer levels also increased the complications in the COVID-19 patient. So it is necessary to continuously monitor D-dimer levels and labelled anticoagulation as management tools for COVID-19 disease to prevent complications and reduce interventions.
Keywords: Venous thrombotic events, D-Dimer, COVID -19
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Microbiologist, Sagar hospital, Bangalore, Karnataka, India. Email: |
Manasa S, Vikram H C V. Analysis of D-Dimer Levels among Covid -19 Positive Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangalore. Int J Med Res Rev. 2021;9(2):82-86. Available From https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/1250 |


 ©
©