Cardiac evaluation of Covid-19 patients with post-discharge dyspnoea
Panda S.1*, Kumar Sharma S.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2020.i06.11
1* Sibaram Panda, Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology, Veer Surendra Sai Institute Of Medical Sciences And Research, Burla, Orissa, India.
2 Sunil Kumar Sharma, Professor and Head, Department of Cardiology, Veer Surendra Sai Institute Of Medical Sciences And Research, Burla, Orissa, India.
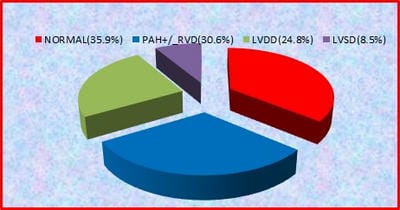
Background: Dyspnoea is one of the common symptoms in COVID-19 patients after discharge from the hospital. So evaluation of cardiac function becomes necessary in COVID patients after hospital discharge. AIM: To study the cardiac function of COVID 19 patients presenting with dyspnoea after discharge from hospital within 3 months of symptom onset. Materials and methods: 245 post-hospital discharge COVID-19 patients enrolled in the study. The patients with abnormal echocardiography are further divided into three groups, A) patients with PAH±RVD, B) patients with LV diastolic dysfunction C) patients with LV systolic dysfunction. Data of the three groups were compared. Results: Out of 245 patients, 64% (157) patients show abnormal echocardiogram.75 (30.6%) patient show PAH±RVD,61(24.8% ) patients shows LV diastolic dysfunction and 21(8.57%) patients shows LV systolic dysfunction. patients with ventricular dysfunction significantly associated with multiple risk factors and comorbidity. Grade 1,2,3,4 diastolic dysfunction seen in 27.8%,34.4%,29.5%,8.1% in group B respectively. LV systolic dysfunction is mild in 13 (61.9%), moderate in6(28.5%), severe in 1 (4.7 %) in group C patients. Ntprobnp, tropnin significantly higher in all groups. Also, CRP, D dimer significantly higher in group A, but non significantly higher in group B, C. Conclusion: RV dysfunction is the most common pattern seen in around 30% of patients. LV diastolic dysfunction is not uncommon, seen in ¼ the patients. Patients with cardiac dysfunction have a high level of cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, which can lead to grievous cardiovascular complications. So close follow up required.
Keywords: Dyspnoea, COVID, PAH with RV dysfunction, Systolic dysfunction, Diastolic dysfunction
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology, Veer Surendra Sai Institute Of Medical Sciences And Research, Burla, Orissa, India. Email: |
Panda S, Sharma SK. Cardiac evaluation of Covid-19 patients with post-discharge dyspnoea. Int J Med Res Rev. 2020;8(6):434-439. Available From https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/1228 |


 ©
©