Prevalence of hyperuricemia in cerebrovascular accidents and its correlation with their outcome
Kori P.1, Chouhan M.2, Singh Mandloi S.3*
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2021.i04.10
1 Preeti Kori, Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Government Medical college, Ratlam, Madhya Pradesh, India.
2 Mahendra Chouhan, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Government Medical college, Ratlam, Madhya Pradesh, India.
3* Sohan Singh Mandloi, Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Government Medical college, Ratlam, Madhya Pradesh, India.
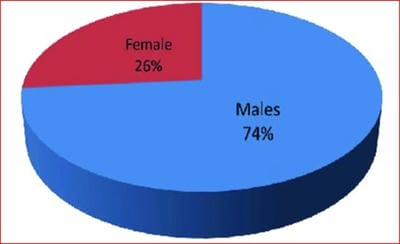
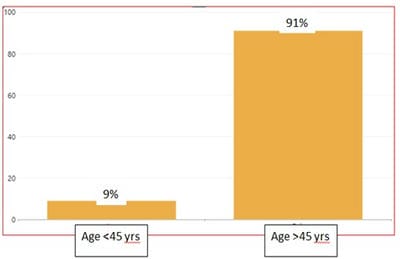
Introduction: Cerebrovascular accident or stroke is a disease of the vascular system of the brain. According to ICD 11, stroke is classified as a neurological disease and not under the circulatory system. It is the second leading cause of death worldwide. It cannot be said that high Serum Uric Acid [SUA] amongst patients with cerebrovascular accidents is directly correlated with their outcome. The present study planned to estimate uric acid levels and their association in acute stroke patients, both ischemic and hemorrhagic. Method: A total of 100 stroke patients admitted under the neurology department were included in the study. Brain imaging (CT/MRI) was performed. The serum uric acid was estimated. Results: Out of a total of 100 patients, 74 were males, and 26 were females. Nine patients were less than 45 years old and 91 patients were 45 and above. Thirty-nine patients had ischemic, and 61 patients had a hemorrhagic stroke, respectively. Out of 100 patients, 23 patients had normal uric acid levels (<7mg/dl). Seventy-seven patients were with high uric acid levels. The mean serum uric acid concentration in male patients was 8.48±2.7and 9.20±2.7 in females. Among the total 100 cases, 69 survived, and the remaining 31 were among the non-survivor group at the time of discharge. Mean serum uric acid in stroke survivors was 8.5±2.6 mg/dl, while in non-survivors, it was 8.6±2.2 mg/dl. There was no significant difference between the levels of uric acid among survivors and non-survivors. Conclusions: The prevalence of hyperuricemia (>9mg/dl) amongst stroke patients was 77% in the present study. The values of serum uric acid were significantly elevated in the patients aged > 45 years. The serum uric acid values were high among the group of hyperglycemic and hypertensive patients at the time of admission. There was no significant difference between the levels of uric acid among survivors and non-survivors.
Keywords: Serum uric acid, Ischemic Stroke, Hemorrhagic Stroke
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Government Medical college, Ratlam, Madhya Pradesh, India. Email: |
Preeti Kori, Mahendra Chouhan, Sohan Singh Mandloi, Prevalence of hyperuricemia in cerebrovascular accidents and its correlation with their outcome. Int J Med Res Rev. 2021;9(4):269-273. Available From https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/1322 |


 ©
©