Role of Multiparametric MRI in Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Mathur M.1, Bains R.2*, Kaur R.3, K. Badhan R.4, Sachin K.5, Mittal D.6
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2019.i02.13
1 Manoj Mathur, Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab, India.
2* Rohan Bains, Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab, India.
3 Ramanpreet Kaur, Junior Resident, Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab, India.
4 Rajesh K. Badhan, Senior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab, India.
5 Sachin K, Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab, India.
6 Dimple Mittal, Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Patiala, Punjab, India.
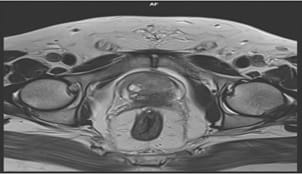
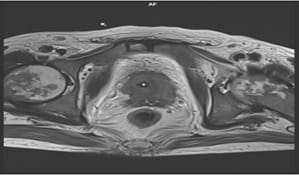
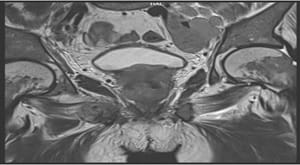
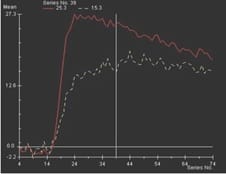
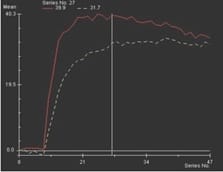
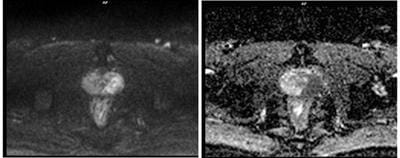
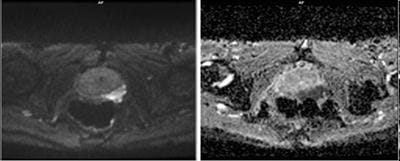
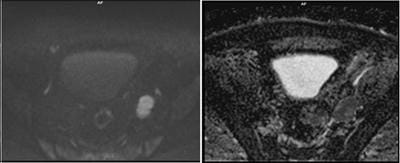
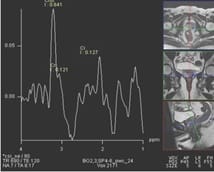
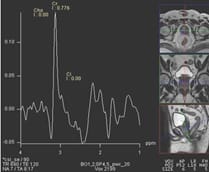
Aims: The main objectives of our study were to evaluate the role of Multiparametric MRI (mp-MRI) in diagnosis of carcinoma prostate and to compare the various MRI sequences used in MRI in evaluating carcinoma prostate with histopathological diagnosis kept as reference standard. Materials and Methods: This prospective cross-sectional study of 40 patients was performed by using various sequences used in mp-MRI i.e. T2 weighted imaging (T2WI), Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI), Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) and Dynamic Contrast Enhanced study (DCE). Findings of mp-MRI sequences were compared with histopathological diagnosis. Statistical analysiswasperformed using SPSS computer statistical program for window release 16. Results: Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) of DCE in diagnosing carcinoma prostate were 88.89%, 50.00%, 94.12% and 33.33% respectively where assensitivities, specificities, PPVs, NPVs of DWI and MRS were same in our study i.e. 94.44%, 75.00%, 97.14% and 60.00%respectively. Overall sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV of mp-MRI by combining these sequences were found to be 97.22%, 75%, 97.22% and 75% respectively. Diagnostic accuracies of DWI, DCE and MRS were 92.5%, 85% and 92.5% respectively and overall diagnostic accuracy after combining these sequences in mp-MRI was 95%. Conclusions: mp-MRI including all the sequences has very good role in evaluation of carcinoma prostate. Diagnostic accuracy of mp-MRI increases when all sequences used together to assess prostatic lesions, so all the sequences should be used together in prostate cancer evaluation rather than using individual sequences.
Keywords: T2 weighted imaging, T1 weighted imaging, Diffusion weighted imaging, Dynamic contrast enhanced imaging, MR spectroscopy
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Patiala, Pubjab, India. Email: |
Mathur M, Bains R, Kaur R, Badhan RK, Sachin K, Mittal D. Role of Multiparametric MRI in Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Int J Med Res Rev. 2019;7(2):130-138. Available From https://ijmrr.medresearch.in/index.php/ijmrr/article/view/1046 |


 ©
©